CacoReady Plates Aid Discovery of Novel HDAC Inhibitors for Prostate Cancer
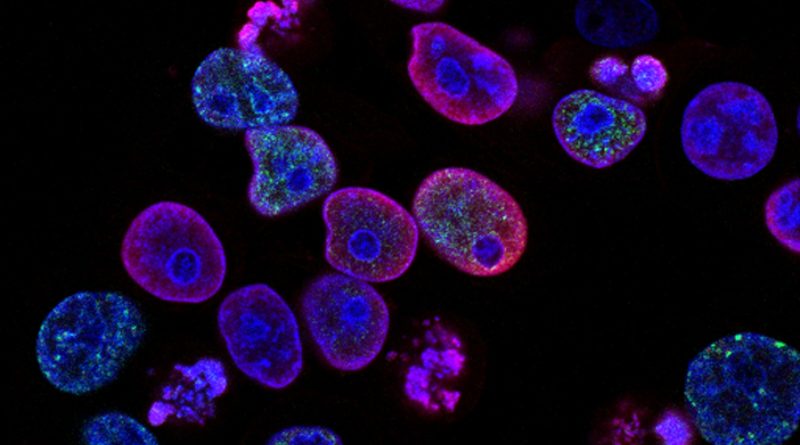
Cutting-edge CacoReady Cell-based Plates with pre-developed Caco-2 cells for in vitro permeability assessment have been a key tool in a study to aid the discovery of novel HDAC Inhibitors for targeting advanced prostate cancer.
A groundbreaking collaborative research endeavor spearheaded by scientist Davide Moi and conducted in affiliation with the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Italy, has been unveiled recently in the esteemed European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (Volume 260, 15 November 2023, 115730). The research paper was published under the compelling title “Discovery of potent pyrrolo-pyrimidine and purine HDAC inhibitors for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer“, where a compound (number 13) that combines potent inhibitory activity and class II selectivity with favorable drug-like properties, was found to be an excellent lead candidate for further optimisation.
This comprehensive investigation incorporates cutting-edge methodologies, including the utilisation of CacoReady plates, a unique ReadyCell product with a pre-developed Caco-2 cell-based model on ready-to-use transwell plates, to appraise the in vitro permeability of HDAC inhibitors. The outcomes not only underscored promising efficacy against prostate cancer cells but also hinted at a prospective avenue for developing innovative treatment strategies.
New Avenues in Prostate Cancer Treatment: Designing HDAC Inhibitors to Precision-Target HDAC6 Activity
Revolutionising the landscape of HDAC inhibitor design with a focus on targeting HDAC6 activity, the study sheds light on the pivotal role of HDACs (histone deacetylases) in gene expression regulation through acetylation/deacetylation of lysine residues in histones and non-histone proteins. Given their involvement in critical cellular processes such as cell cycle progression, differentiation, and apoptosis, HDACs emerge as particularly intriguing in the context of prostate cancer, where they modulate the androgen receptor (AR), a key driver of cancer progression and drug resistance.
Promising Findings: Lead Candidate Superior Selectivity and Minimal Toxicity
The primary objective of this research was the conceptualisation and synthesis of novel HDAC inhibitors across three distinct series, with a pronounced emphasis on HDAC6 inhibitory activity. The compounds underwent meticulous evaluation for their impact on aggressive prostate cancer cell proliferation, tumor selectivity, anti-migration properties, and in vitro drug-like characteristics. Notably, among the array of synthesized compounds, compound 13 demonstrated remarkable efficacy, positioning itself as a promising lead for subsequent research endeavors due to its elevated selectivity and minimal toxicity.
Utilising Caco-2 Cell-based Plates for In Vitro Permeability Assessment
An integral facet of the study design was the assessment of in vitro permeability, employing CacoReady cell-based plates to unravel the mysteries of cellular adsorption. The Caco-2 cells (ECACC), which are pre-plated after 21 days of culture were acquired from the innovative Barcelona-based company ReadyCell.
By quantifying the permeability of the synthesised compounds within Caco-2 cells, researchers discerned the compounds that exhibited superior cellular adsorption. These findings exposed variations in cell membrane permeability among the compound series, hinting at a potential trade-off between heightened in vitro HDAC6 inhibitory activity and reduced cell permeability.
Consequently, the study concluded that a strategic optimisation of lead hydroxamic acid derivatives is imperative to strike a delicate balance between in vitro potency and cell permeability. This insight not only advances our understanding of the intricate dynamics of HDAC inhibitors but also paves the way for refined therapeutic approaches in the ongoing battle against advanced prostate cancer.
The study by Davide Moi in affiliation with the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Italy delves into the nuanced potential of HDAC inhibitors for advancing prostate cancer treatment. The findings imply a pivotal role for HDAC inhibitors in shaping the trajectory of future prostate cancer therapy, extending the influence of this study even beyond its initial focus. The CacoReady ready-to-use Caco-2 cell-based plates used in this research have proven to be an important aid to scientists in accelerating their research.